Fixed Frame Screen – Transform your living room or dedicated media space into a reference-quality home theater with our premium Slim Bezel Acoustically Transparent Fixed Frame Screen—engineered for audiophiles, cinephiles, and luxury smart home integrators who demand uncompromised audiovisual performance.
Unmatched Acoustic Transparency Meets 4K/8K Visual Fidelity
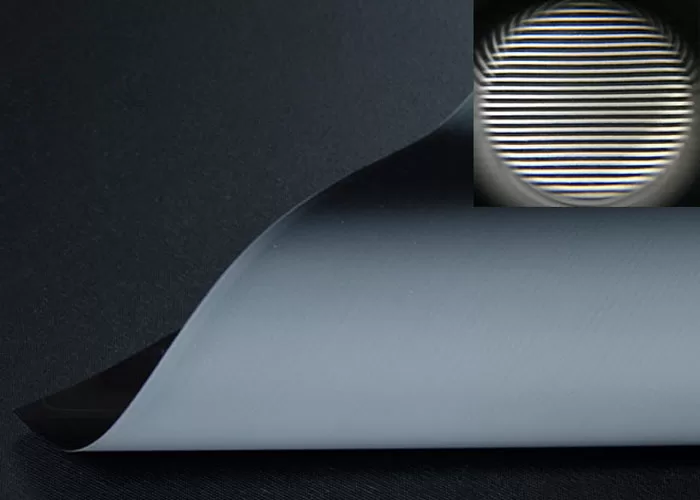
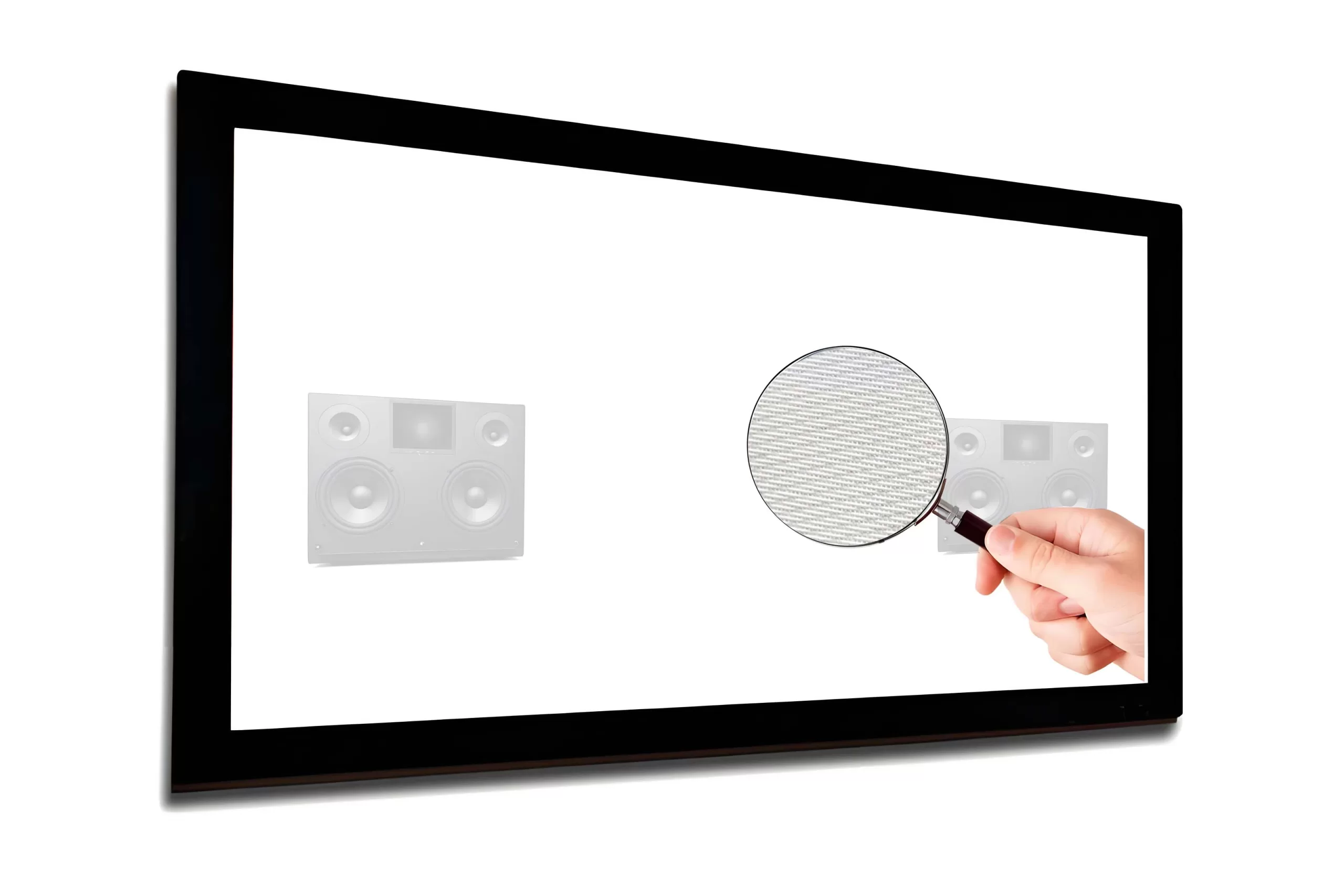
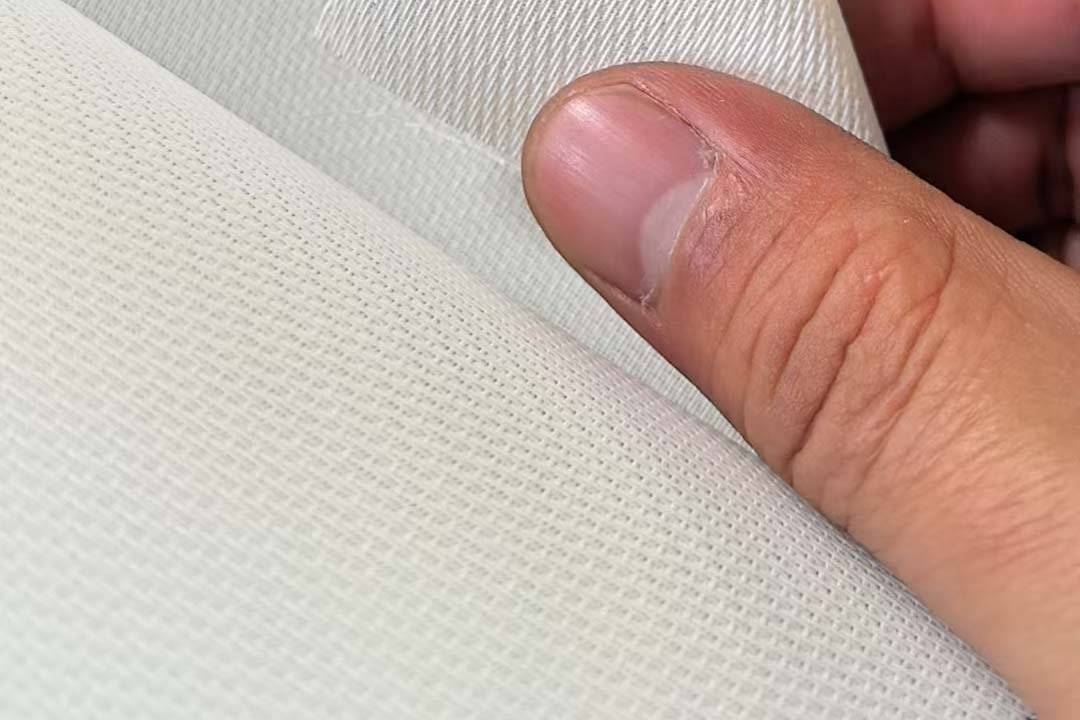
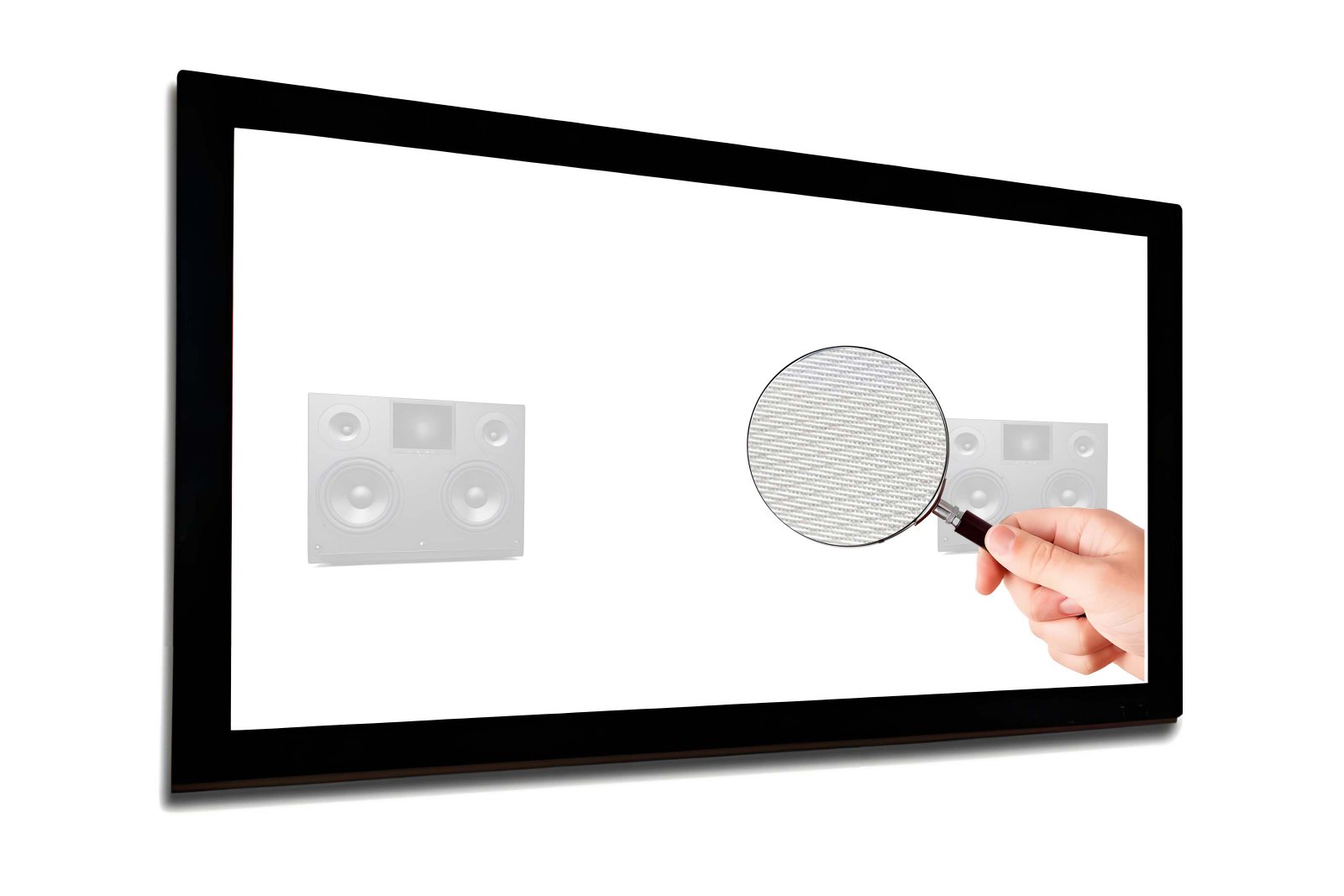
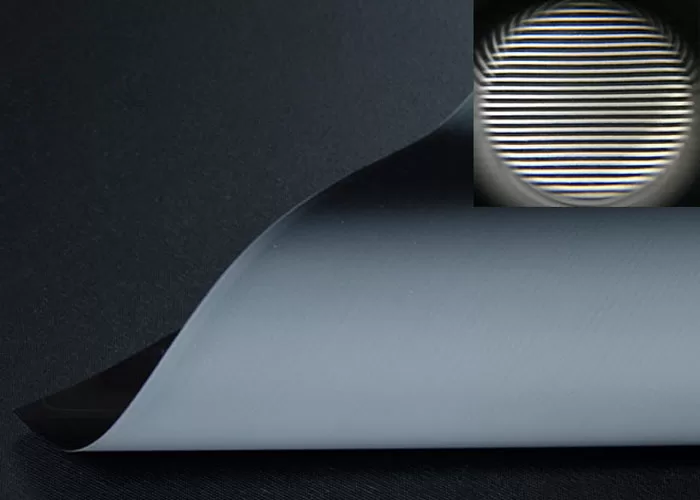
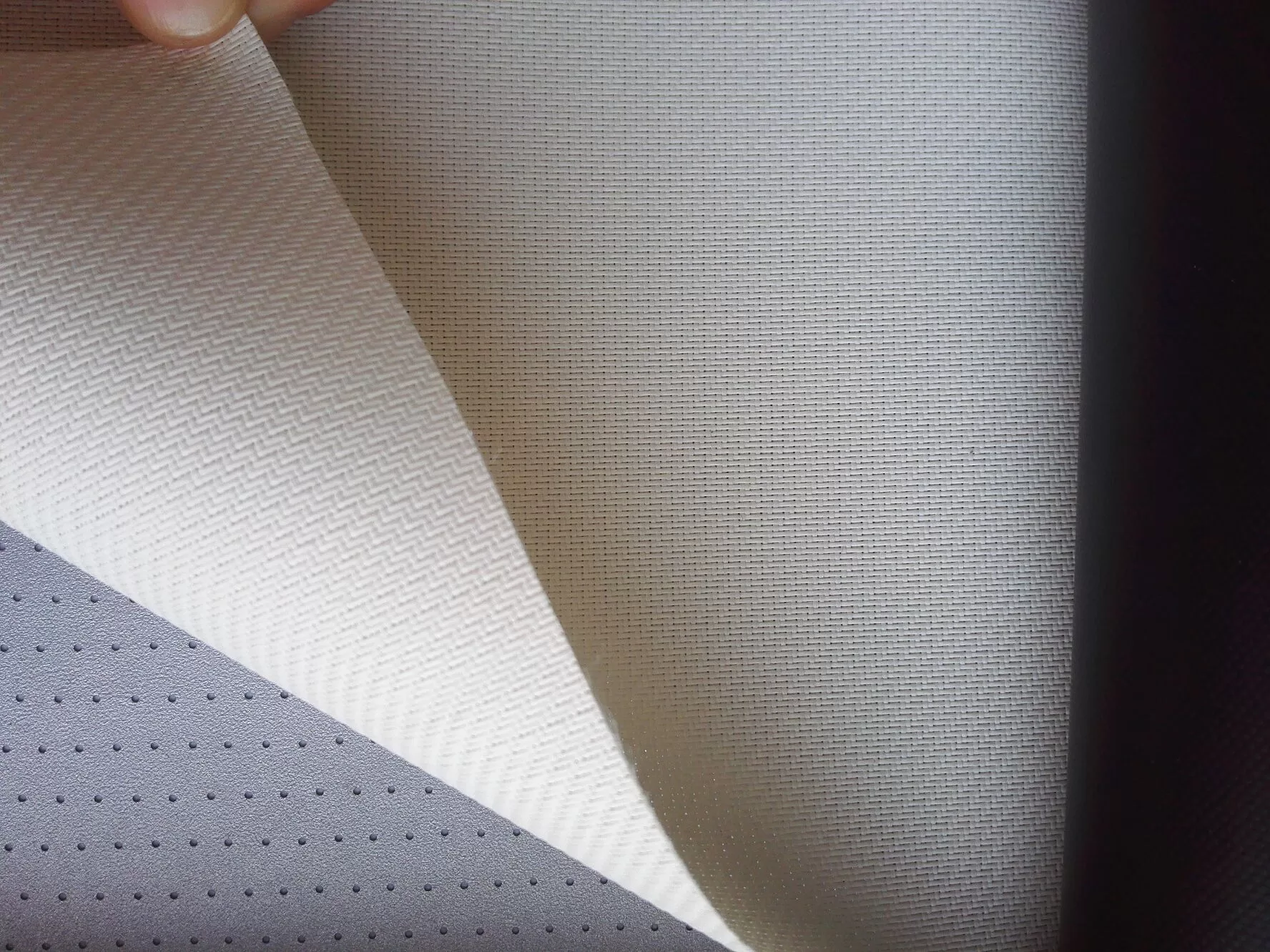
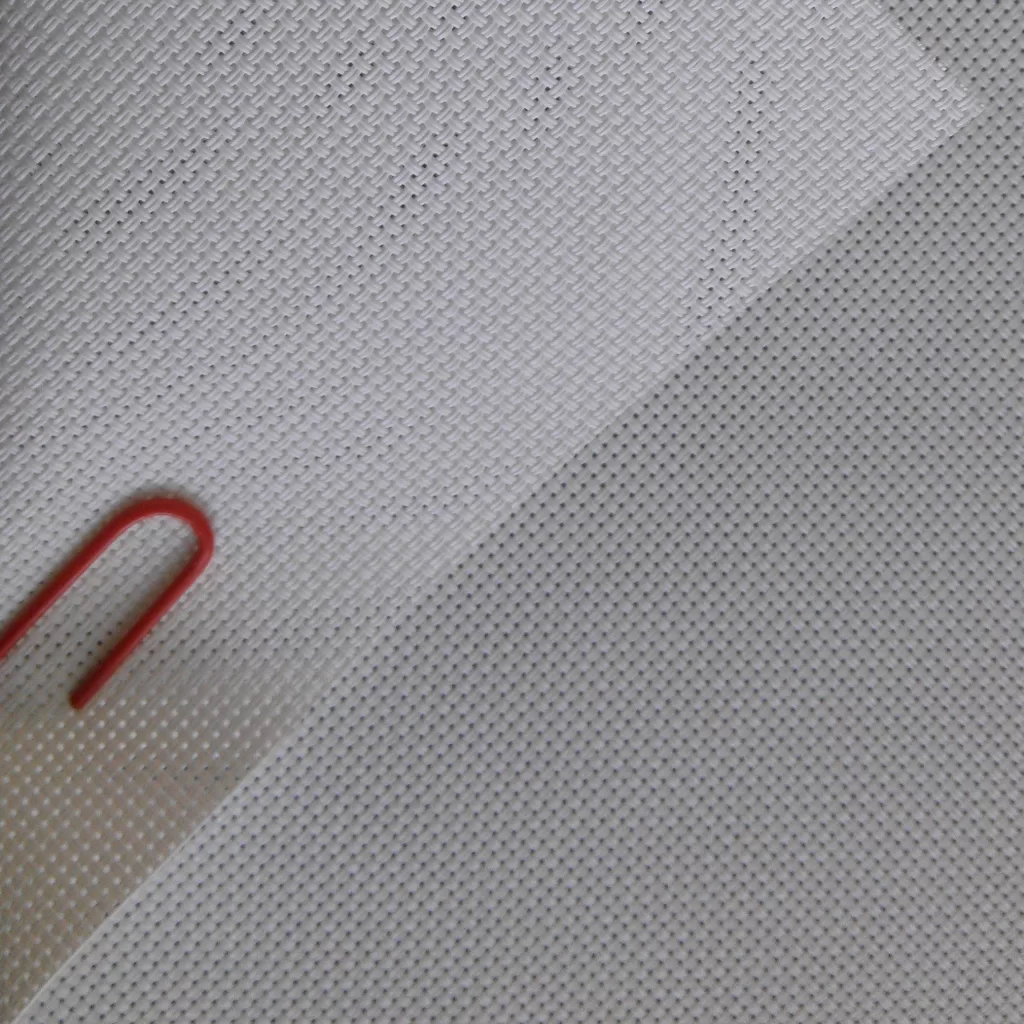
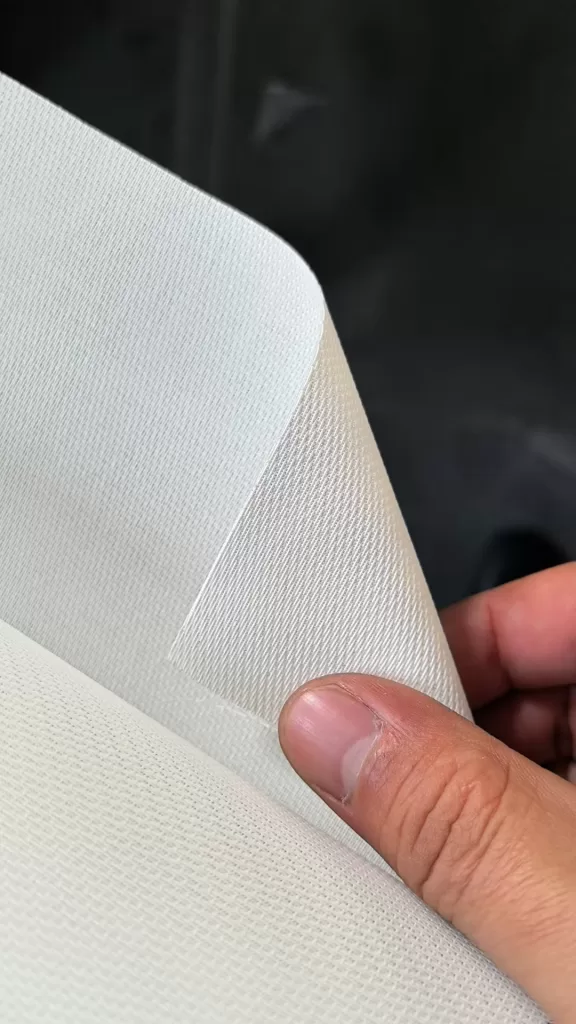
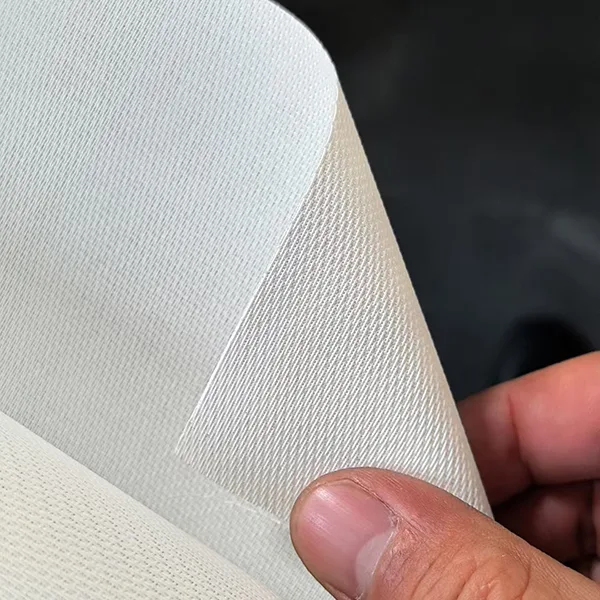
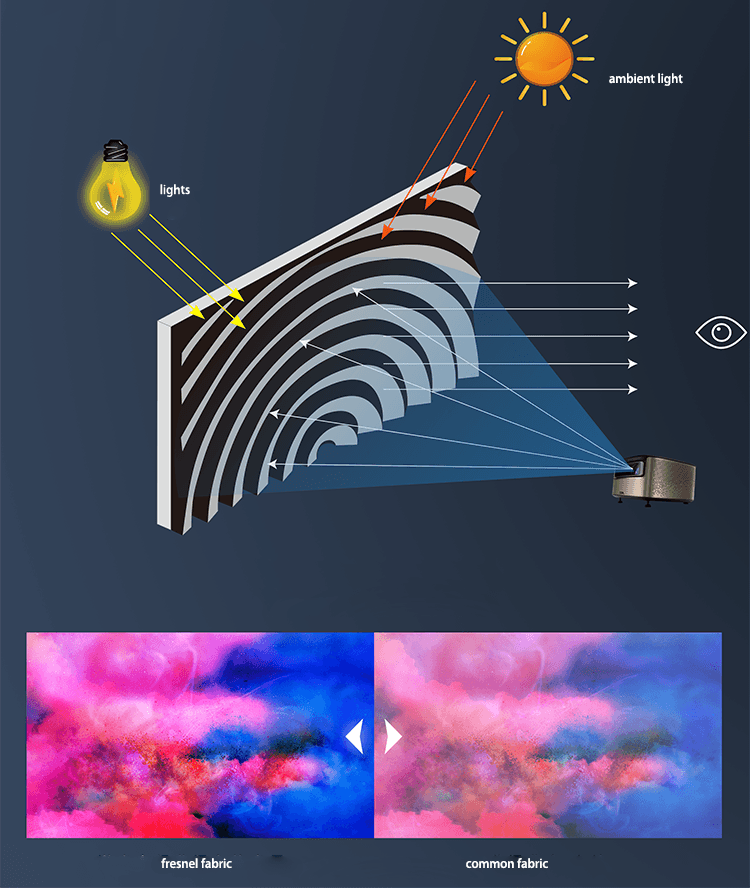
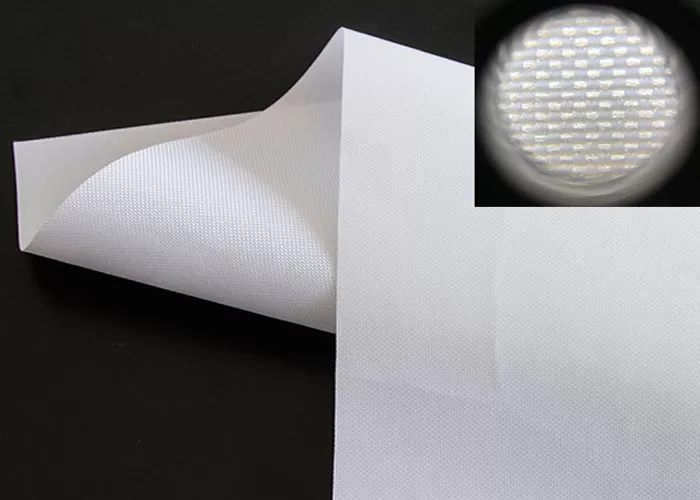
Crafted from advanced woven acoustic screen fabric (not perforated!), this screen delivers 95% acoustic transparency, allowing front LCR speakers—including in-wall or on-wall models—to be seamlessly placed behind the screen without signal loss or coloration. Unlike traditional perforated projection screens with visible holes that degrade image quality, our micro-perforated acoustic fabric features ultra-fine 0.3mm micro-holes, ensuring zero moiré pattern, neutral color balance, and full compatibility with 4K, 8K, HDR, and Dolby Vision content.
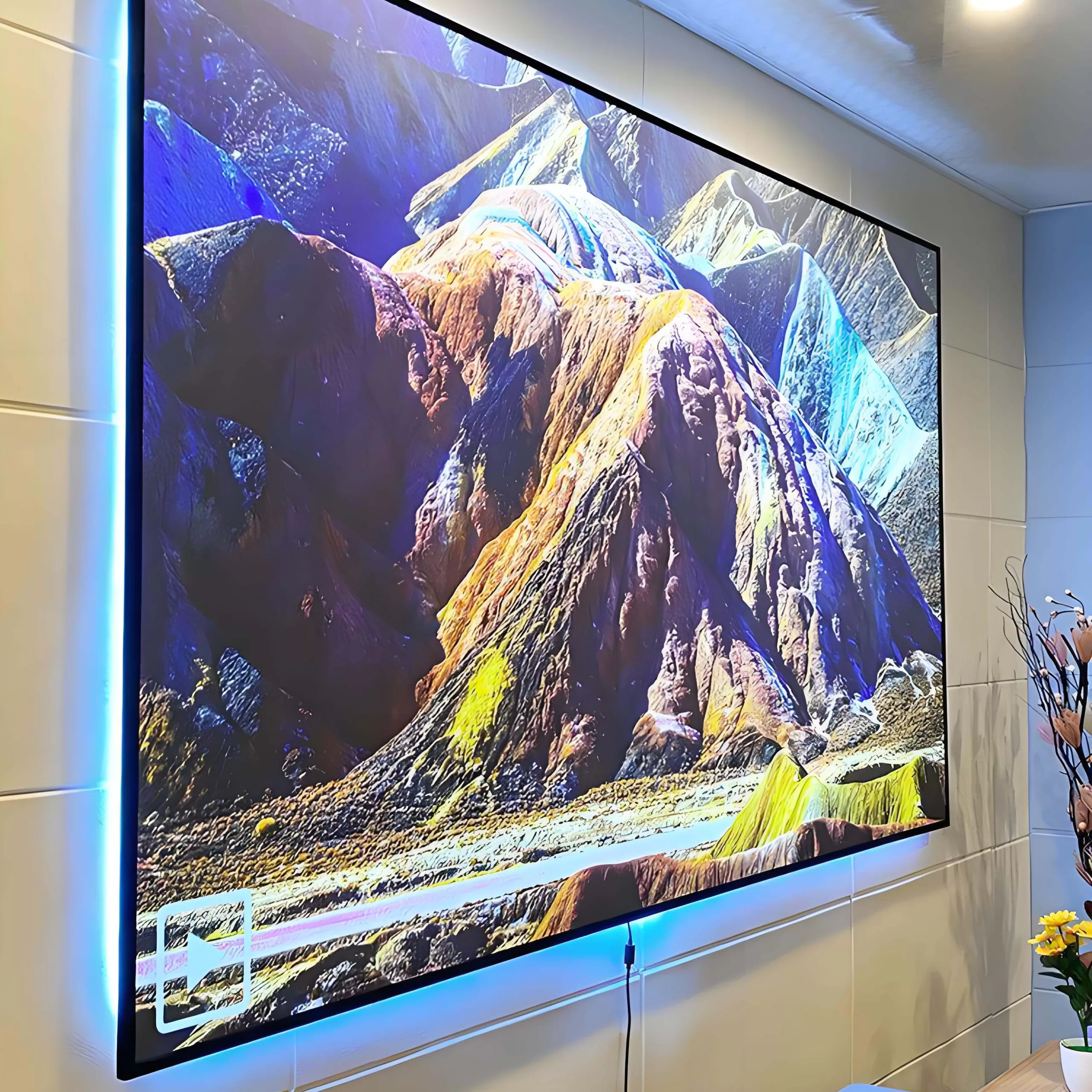
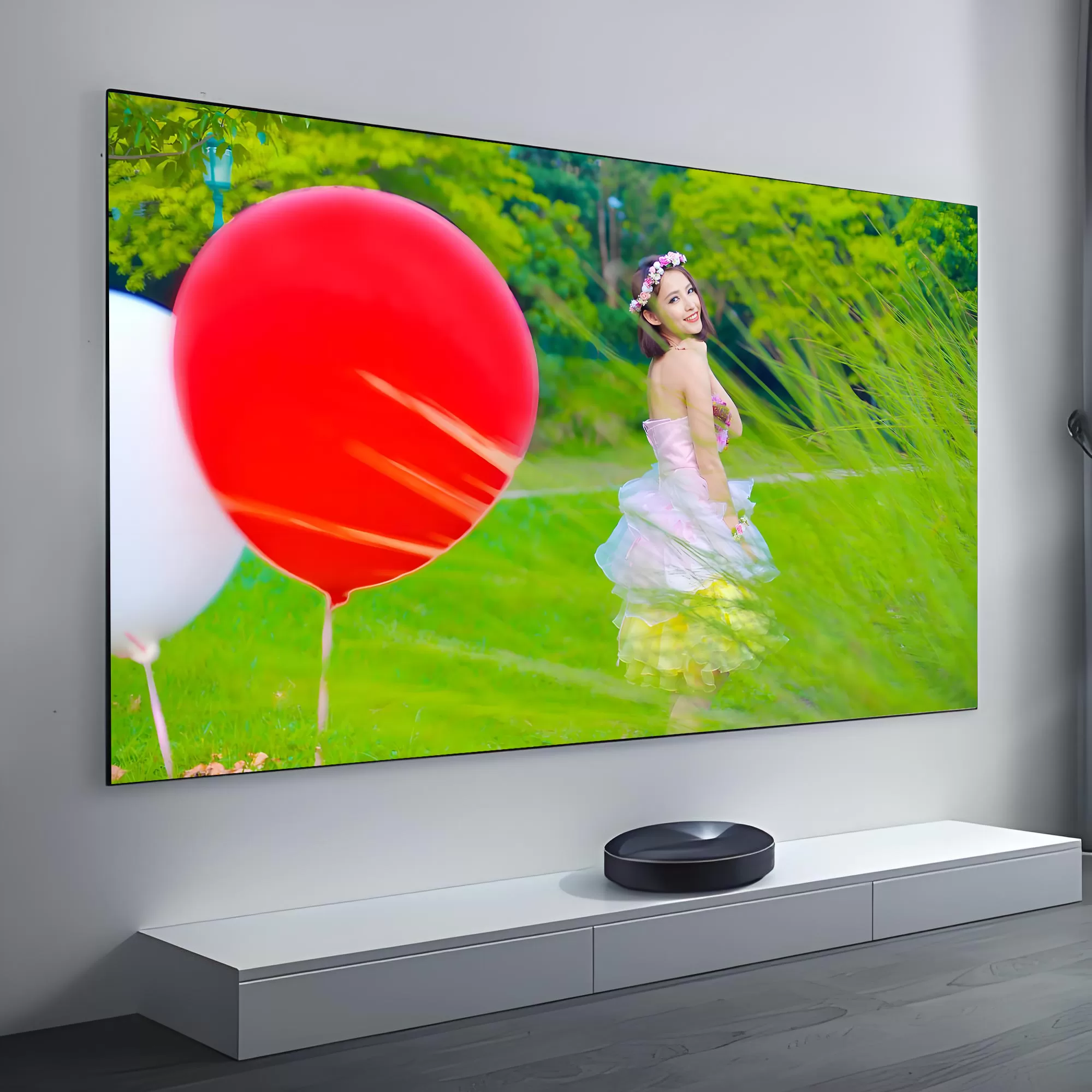
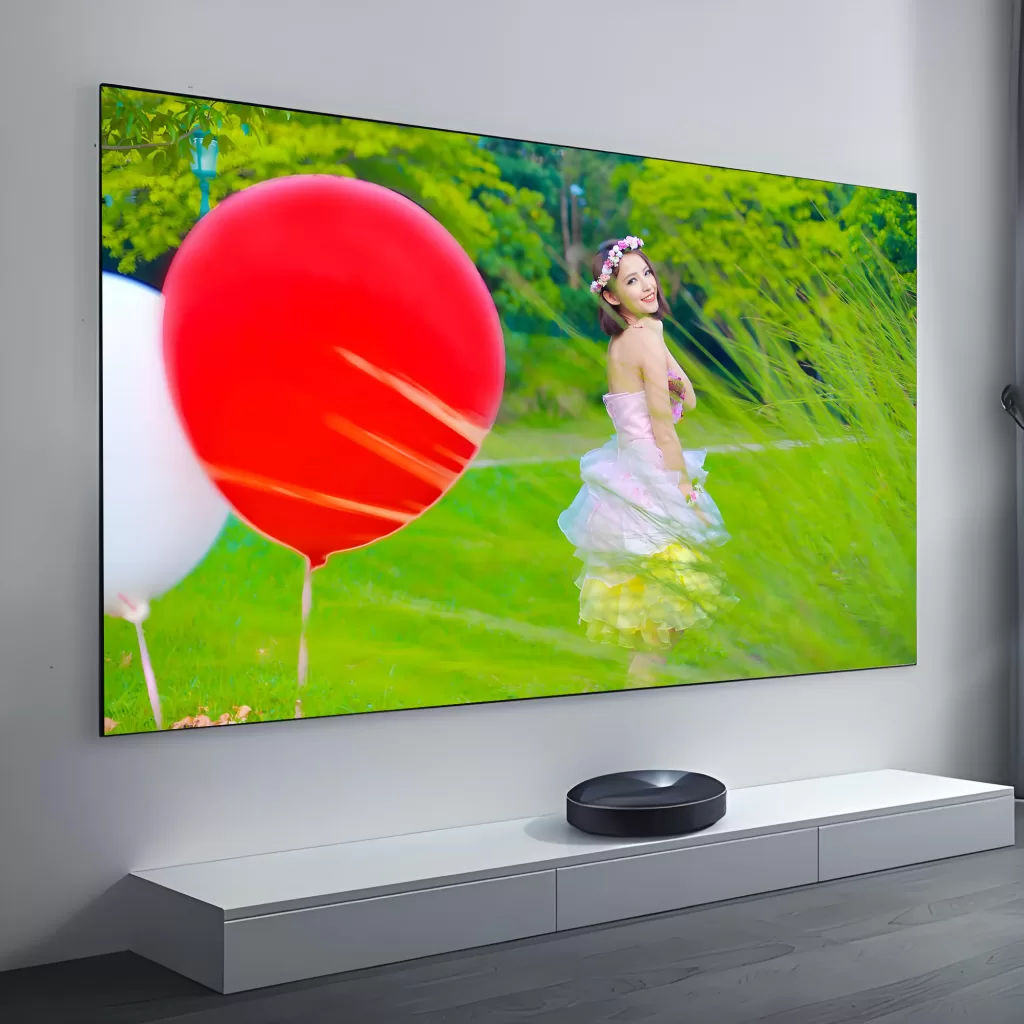
The result? A pristine, immersive picture with lifelike contrast and brightness—perfectly paired with crystal-clear, unobstructed sound from your high-end speaker system.
Sleek, Modern Design for Discreet Integration
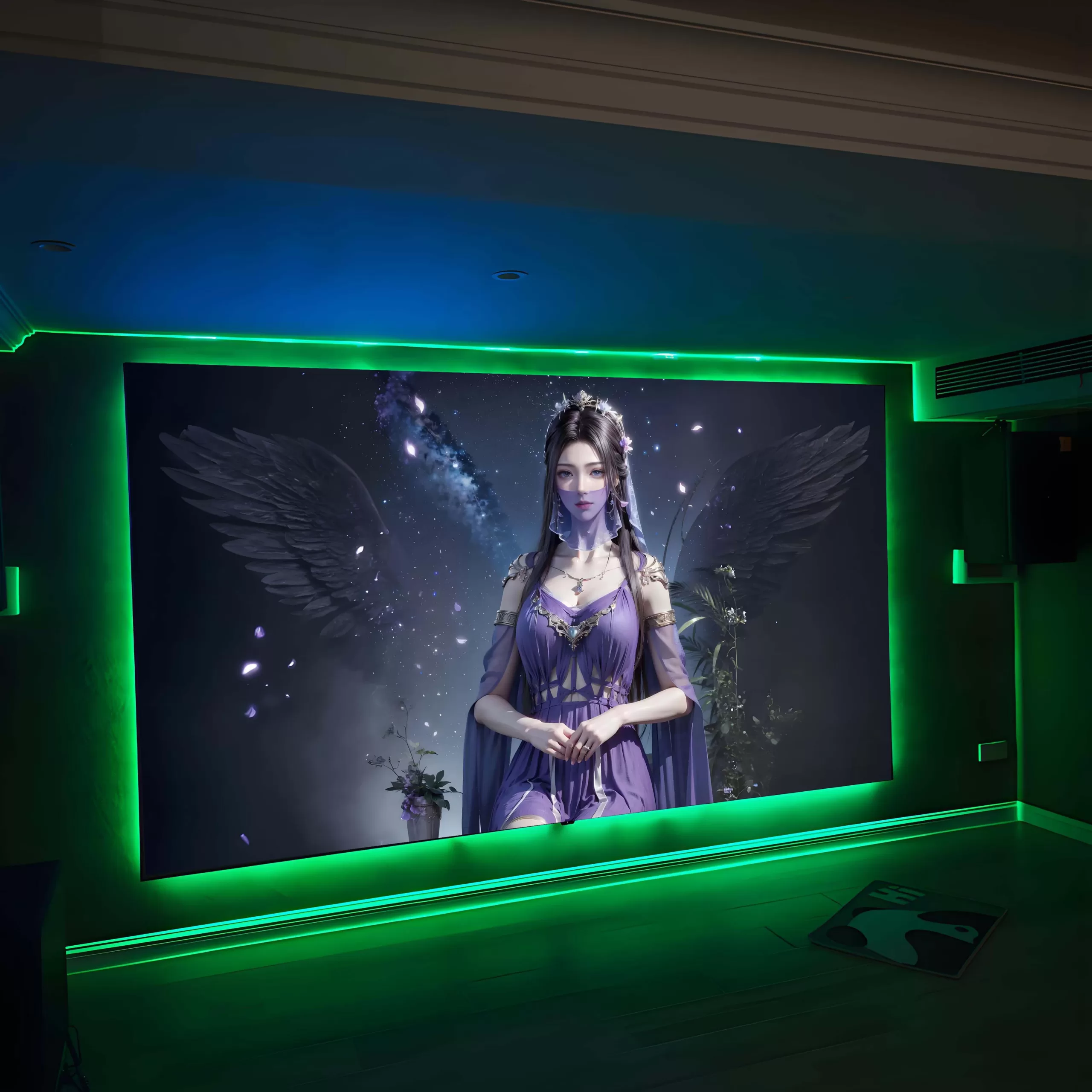
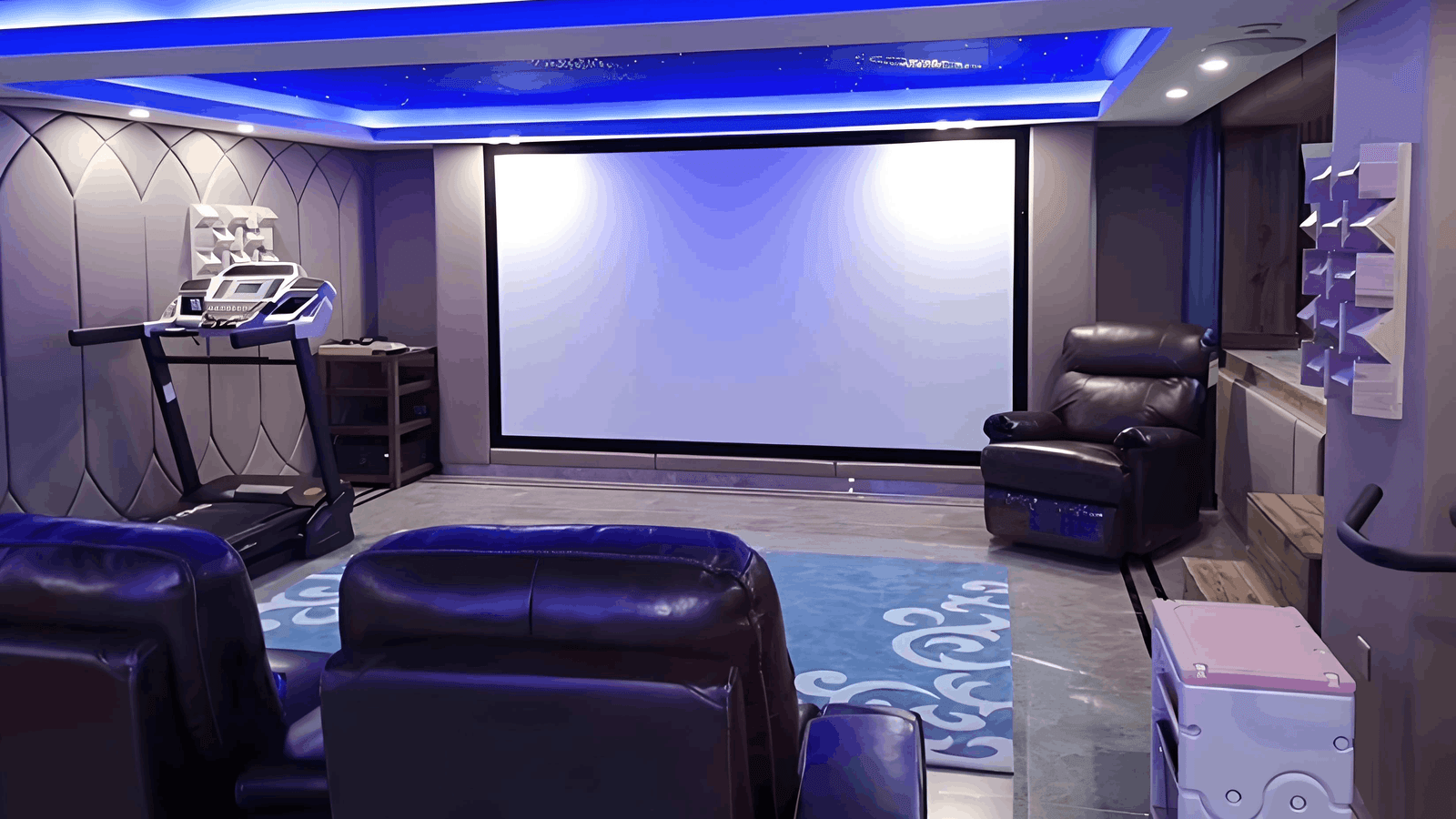
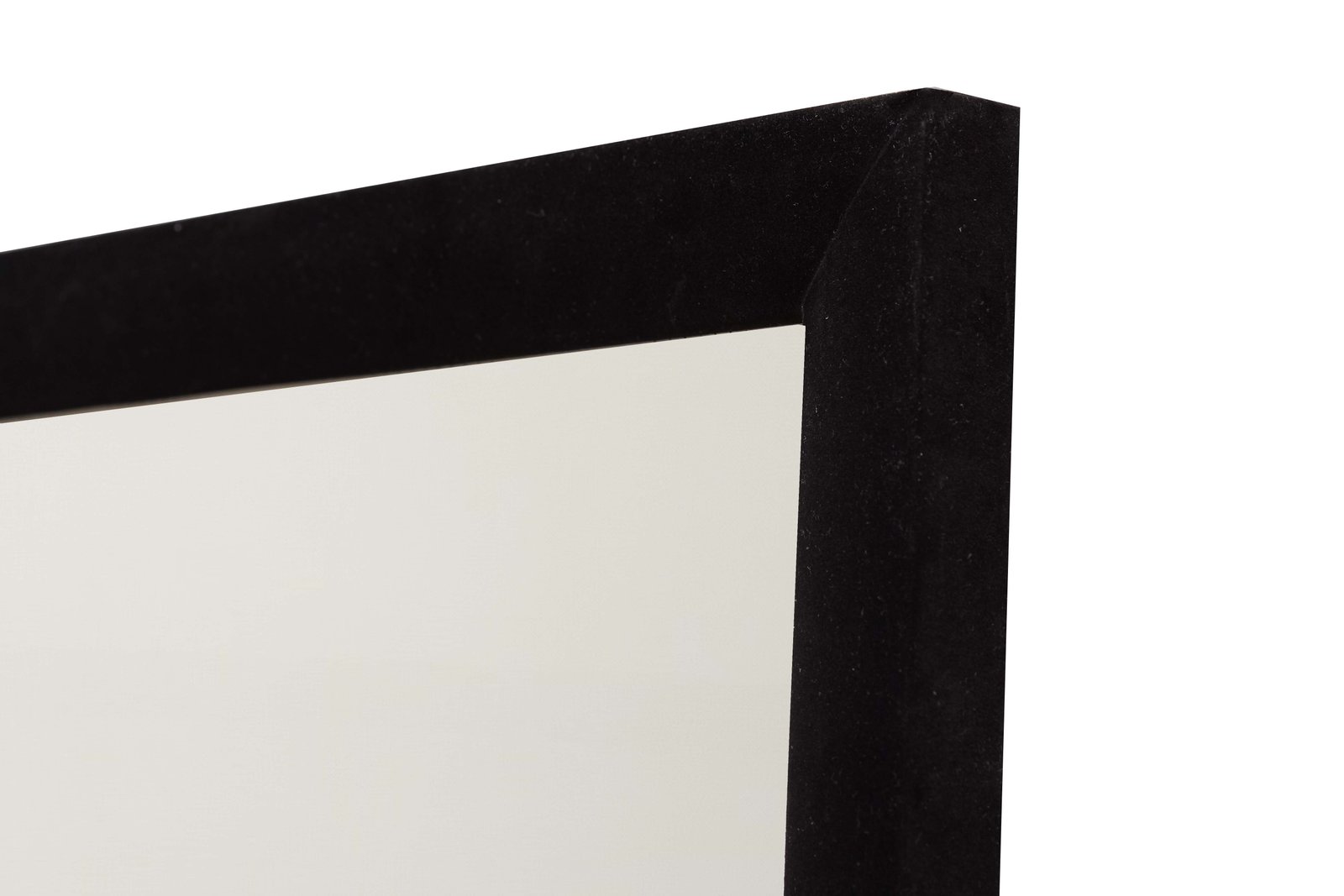
Designed with minimalist aesthetics in mind, our slim bezel acoustic transparent screen offers a near-frameless appearance that blends effortlessly into modern interiors. Whether mounted flush in a custom media wall or showcased as a statement piece in a multi-purpose living room cinema, the clean lines and matte white finish ensure visual elegance without distraction.
Available in custom sizes (including popular formats like 120″ 16:9), each screen features a tensioned acoustic transparent surface for perfect flatness and long-term stability—critical for laser and high-lumen projectors like Sony VPL-VW, Epson LS series, and LG CineBeam.
Engineered for High-Performance Home Theater Setups
This screen is purpose-built for advanced AV installations:
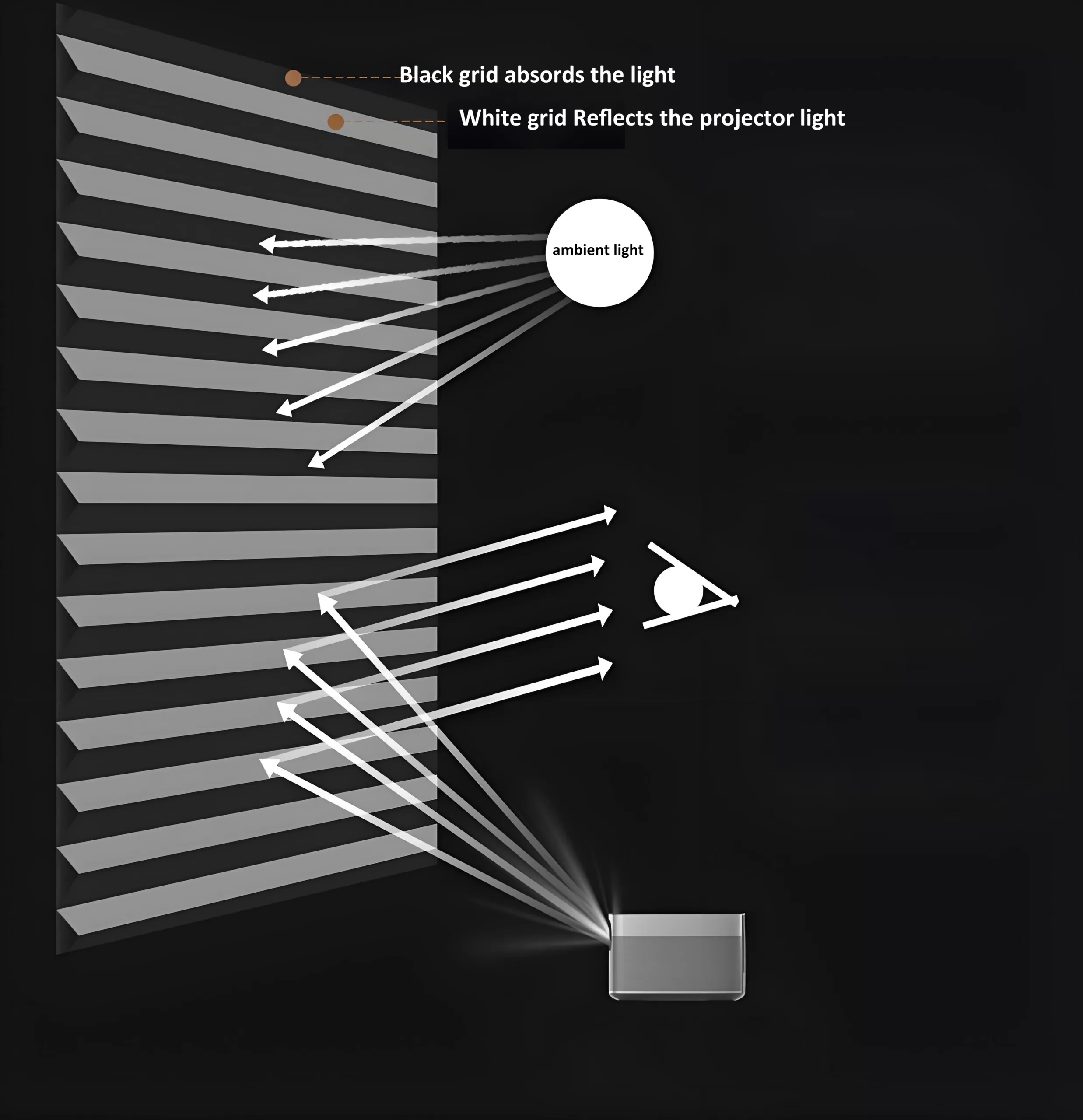
- Black backing / light trap backing prevents ambient light bleed and enhances contrast
- Dual-layer AT fabric option available for superior ambient light rejection
- Fully compatible with Dolby Atmos and front speaker behind screen configurations
- Ideal for hidden speaker home cinema solutions where design and performance must coexist
Whether you’re integrating in-wall speakers, building a luxury smart home theater, or seeking a reference-quality cinema screen comparable to industry benchmarks like Seymour AV Center Stage XD or Stewart Filmscreen StudioTek 130 AT, our woven AT screen delivers elite performance at a competitive price.
FAQ Highlights
❓ Can you really put speakers behind the screen?
Absolutely! Our woven fabric allows full-range audio to pass through with minimal attenuation—ideal for LCR (Left-Center-Right) speaker placement directly behind the screen.
❓ Does an AT screen reduce picture brightness?
There is a slight gain reduction (~10–15%) compared to non-AT screens, but our high-transparency fabric and neutral gain (1.0–1.1) preserve brightness while maintaining color accuracy—especially when paired with modern high-lumen projectors.
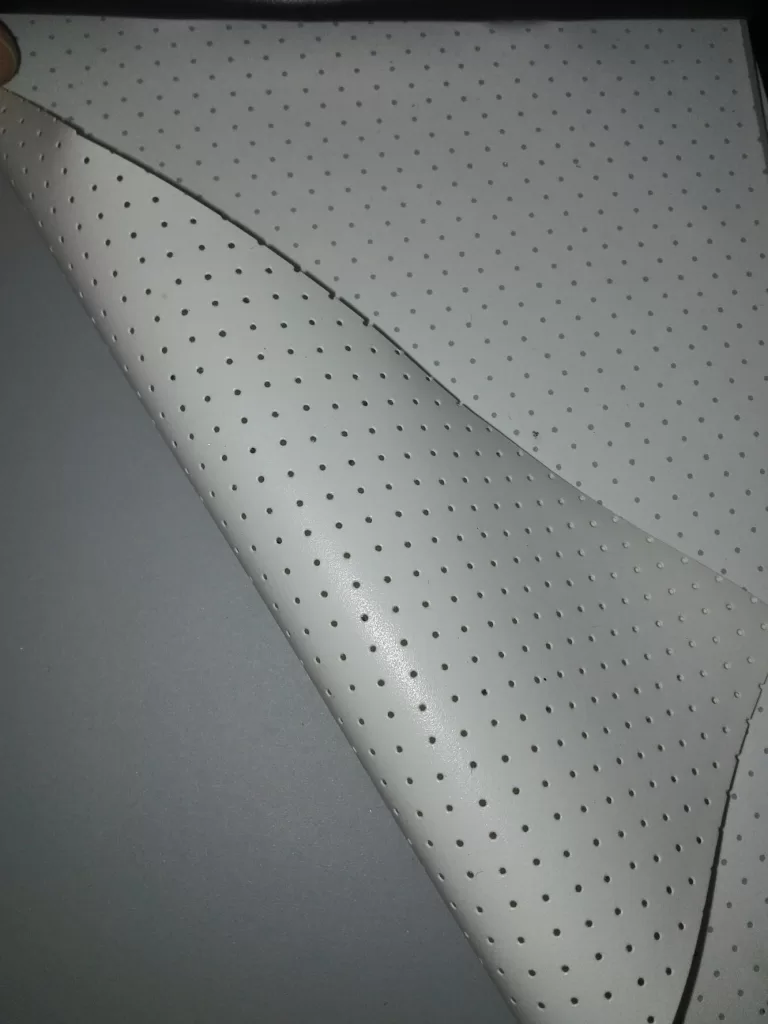
❓ Woven vs. perforated: what’s the difference?
Woven fabrics use interlaced micro-fibers to create invisible acoustic pathways, eliminating visible holes and moiré. Perforated screens drill physical holes, often degrading image quality—especially with 4K laser projectors. We use only premium woven materials for true high-end performance.
Ready to Elevate Your Home Theater?
Choose the screen that professionals trust: a slim bezel, woven, acoustically transparent fixed frame screen engineered for 4K HDR, in-wall speaker compatibility, and seamless integration into the most discerning AV environments.
Compatible with Sony, Epson, JVC, LG, and more. Custom sizes available. Matte white finish. 95% acoustic transparency. Zero moiré. Home theater ready.